Imagine the world in 2023 where all the monetary transactions are still done by cheque! Very hard to imagine, especially because we live in a global, e-commerce economy. Without electronic funds transfer or EFT, there is no modern 2023!
So, when you make any fund transfer today, we are willing to bet that you’re using EFT technology. But what is electronic funds transfer? Why is it essential for our lives? What are the vulnerabilities of EFT that may be used against us?
Well, that’s what we will focus on in this comprehensive post! Let’s dive in now, shall we?
What is An Electronic Funds Transfer–EFT Payment?
An EFT payment simply transfers money electronically from one bank account to another without needing paper documents. It’s like sending cash through the digital realm!
EFT payments have become popular because they are easy to use, convenient, and don’t require you to rely on bank employees. Everything from ATMs to phone payments like Paypal or Bkash is a type of EFT technology.
One of the great things about Electronic Funds Transfer- EFT payments is that they are much faster and more efficient than traditional payment methods like cash or checks.
When you make an EFT payment, the money is transferred immediately, so you don’t have to wait for it to go through. It’s a quick and direct way to send money wherever it needs to go.
Types of EFT Payments
There are different types of EFT payments you might come across. For example, direct deposit, where your paycheck is automatically deposited into your bank account, is an Electronic Funds Transfer-EFT payment.
Using your credit card to pay for something online or at a store is also considered an EFT payment. Even withdrawing cash from an ATM or sending money through a smartphone app to a friend falls under the category of EFT payments.
So, if you’ve ever used online banking to move money between your accounts or sent money to a friend using a mobile payment app, congratulations! You’ve already experienced the convenience of EFT payments. It’s a modern and hassle-free way to handle money and make transactions.
However, every modern consumer, merchant, or business should understand the Electronic Funds Transfer-EFT process well. So, let’s focus on that for a second.
Electronic Funds Transfer Process – How Does It Work?
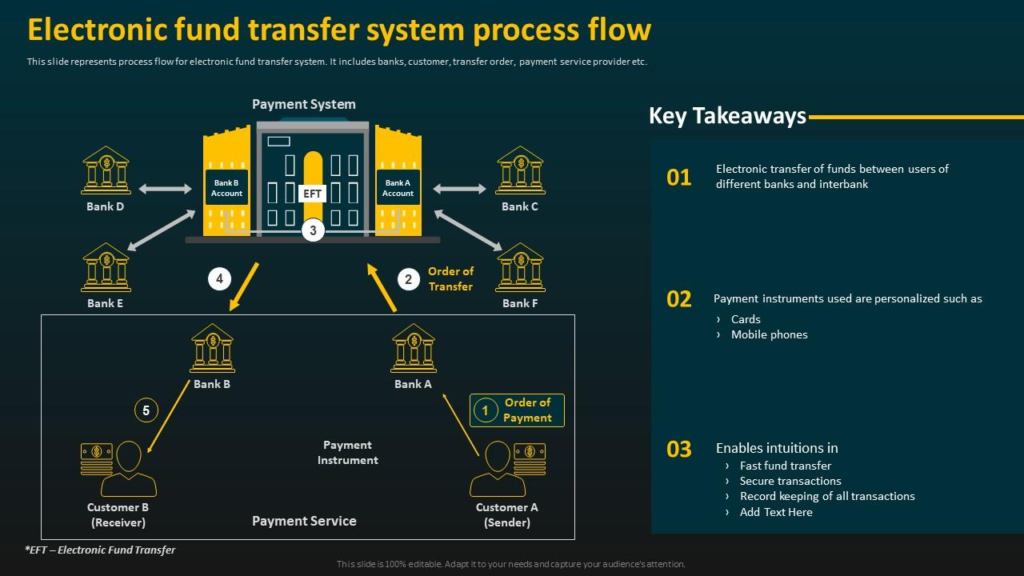
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) involves two parties: the sender and the receiver.
After the sender authorizes the transaction, the EFT request follows through many digital networks and payment terminals. After the sender’s bank receives the EFT request, they transact the money from the sender’s account to the receiver’s bank account.
Then, the sender’s bank sends information to the receiver’s bank that money is being transferred to the receiver’s account, and they automatically adjust their books.
A sender can be a business, an individual, an employee, an employer, or anybody. The same is true for the receiver as well.
Let’s use examples to explore how EFT works and understand money flow across payment networks.
Example 1:
Imagine you need to pay your monthly electricity bill. You make an EFT payment instead of writing a check or using cash.
Here’s how the transaction unfolds:
- Initiating the Transaction: You log in to your online banking portal or mobile banking app and navigate to the payment section. You provide the necessary details, such as the recipient’s account number and the amount you want to pay.
- Sender’s Bank: Your bank receives the payment request and verifies the availability of funds in your account. They authenticate your identity and ensure the transaction is legitimate.
- Payment Network: Once your bank approves the transaction, the payment is sent through a secure payment network. This network acts as a bridge between your bank and the recipient’s bank.
- Receiver’s Bank: The payment network routes the transaction to the recipient’s bank. The recipient’s bank receives the payment instructions and verifies the recipient’s account details.
- Crediting the Receiver’s Account: Upon successful verification, the recipient’s bank credits the amount to the electricity company’s account associated with the provided account number.
- Notification: Both you and the electricity company receive notifications confirming the completion of the transaction. The electricity company updates your account, reflecting the payment made.
Throughout this process, funds transfer occurs electronically, eliminating the need for physical checks or cash.
Example 2:
Let’s say you want to purchase a product from an online retailer. Instead of using a credit card or cash on delivery, you opt for an EFT payment.
Here’s the complete process of this transaction:
- Placing the Order: You browse the online retailer’s website and select the desired product. At the checkout page, you choose the EFT payment option.
- Payment Details: The online retailer provides you with their bank account details, such as the account number and routing number, along with the total amount due for the purchase.
- Initiating the Transaction: You log in to your online banking portal or mobile banking app and navigate to the “Transfer” or “Payments” section. You enter the retailer’s bank account details and the amount to transfer.
- Sender’s Bank: Your bank receives the payment request and performs security checks. They validate your identity, ensure sufficient funds are available, and confirm the transaction’s authenticity.
- Payment Network: Once your bank approves the transaction, it is transmitted through a secure payment network that connects your bank to the retailer’s bank.
- Receiver’s Bank: The payment network forwards the transaction to the retailer’s bank. The retailer’s bank verifies the account details provided and confirms the receipt of funds.
- Order Confirmation: The online retailer receives a notification of the successful payment. They update their records, confirming that your payment has been received.
- Shipping the Product: The online retailer sends the product to your specified address after receiving the payment. You will receive a confirmation email or tracking information for the shipment.
In this example, the EFT transaction allows you to purchase online without needing physical payment methods.
By transferring funds electronically, you can securely complete the transaction, and the retailer can process and ship your order promptly.
Benefits and Importance of Electronic Funds Transfer in 2023

EFT offers numerous benefits for the financial sector in the modern world. Without EFT transactions, e-commerce and modern business, which ultimately are the soul of the current economy, can not function!
Let’s explore some of the key benefits and why EFT is increasingly important:
1. Convenience and Efficiency
EFT provides unparalleled convenience and efficiency in financial transactions. Individuals and businesses can initiate transfers, make payments, and receive funds electronically with just a few clicks or taps.
This eliminates the need for physical checks, reduces paperwork, and streamlines the entire process. Whether paying bills, transferring salaries, or making online purchases, EFT simplifies transactions and saves time and effort.
2. Speed and Timeliness
One of the significant advantages of EFT is its speed and timeliness. Compared to traditional payment methods like mailing checks or processing cash transactions,
EFT enables the near-instantaneous funds’ transfer between accounts. Payments can be processed and settled quickly, allowing for faster transactions, improved cash flow, and timely disbursement of funds. This is especially crucial in today’s fast-paced world, where promptness is highly valued.
3. Security and Safety
EFT offers enhanced security and safety compared to physical payment methods. With EFT, funds are transferred electronically, reducing the risks associated with lost or stolen checks, cash handling, and potential human errors.
Encryption and robust security measures protect sensitive financial information, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of transactions. Additionally, digital records of EFT transactions provide a transparent audit trail, making it easier to track and reconcile financial activities.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Using EFT can lead to significant cost savings for both individuals and businesses. It eliminates the expenses of producing and processing paper checks, including printing, postage, and manual labor.
EFT reduces administrative overhead, minimizes the need for physical storage of documents, and simplifies accounting processes.
Moreover, businesses can optimize their cash management by leveraging EFT for faster settlement and reconciliation, reducing the costs of handling and managing physical cash.
5. Accessibility and Global Reach
EFT transcends geographical boundaries and enables seamless transactions across banks, financial institutions, and international borders.
It allows individuals and businesses to send and receive funds from anywhere, anytime, using digital platforms or online banking services.
EFT promotes financial inclusion by offering access to banking services for individuals who may not have access to traditional banking facilities, thereby fostering economic participation and empowerment.
Risks of Electronic Funds Transfer and How to Mitigate Them

While Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) offers numerous benefits, it is essential to be aware of potential risks associated with this payment method.
Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies can help ensure a secure and smooth EFT experience. Let’s explore some common risks and ways to mitigate them:
1. Unauthorized Access and Fraud
Risk: Unauthorized access to sensitive financial information or fraudulent activities can lead to unauthorized transfers or use of funds.
Mitigation: Protect yourself by implementing strong security measures. Use secure and unique passwords for your online banking accounts. Enable two-factor authentication for an additional layer of security.
Regularly monitor your accounts for suspicious activity and immediately report it to your bank. Stay vigilant and be cautious of phishing attempts or suspicious emails and websites.
2. Technical Issues and System Failures
Risk: Technical issues, system failures, or glitches can disrupt EFT processes, leading to delays or incorrect transactions.
Mitigation: Choose reputable, reliable financial institutions and payment service providers with robust systems. Keep your software and devices updated to minimize the risk of compatibility issues.
Regularly back up your financial data to ensure you can recover it during system failures. Maintain alternative payment methods as backups for emergencies.
3. Data Breaches and Identity Theft
Risk: Data breaches can compromise personal and financial information, leading to identity theft and unauthorized transactions.
Mitigation: Ensure that your devices, including computers and mobile devices, have installed up-to-date security software and firewalls.
Avoid sharing sensitive information over unsecured networks or websites.
Be cautious of providing personal information to unfamiliar or suspicious sources. Review your credit reports and bank statements for any unusual activity or discrepancies.
4. Payment Disputes and Errors
Risk: Disputes or errors may arise, such as incorrect or incomplete transfers, duplicate charges, or issues with product or service quality.
Mitigation: Keep detailed records of your transactions, including confirmation emails, receipts, and invoices. Review your bank statements regularly to identify any discrepancies or unauthorized charges.
Communicate promptly with your bank or payment service provider to address any issues or disputes. Familiarize yourself with the dispute resolution processes and consumer protection policies your financial institution provides.
5. Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks
Risk: Social engineering and phishing attacks can trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing unintended transactions.
Mitigation: Avoid unsolicited calls, emails, or messages requesting personal or financial information. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Verify the legitimacy of any requests by contacting your financial institution directly through trusted contact information.
Conclusion
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) has revolutionized how we handle financial transactions. It offers convenience, speed, and security. EFT allows easy funds transfer between accounts, eliminating the need for physical checks.
In 2023, EFT provides quick and efficient ways to pay bills, transfer money, and manage finances. While EFT brings many benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks like unauthorized access and fraud.
By taking precautions, such as using strong passwords, staying vigilant for scams, and keeping software updated, we can enjoy the convenience and advantages of EFT while keeping our finances safe.






